Internet Protocol (IP)¶
What is IP?¶
It is a method for sending data from one device to another across the internt. Every device has an IP address that uniquely identifies it and enables it to communicate with and exchange data with other devices connected to the internet.
IP is the main protocol within the internet layer of the TCP/IP. Its main purpose is to deliver data packets between the source application or device and the destination using methods and structures that place tags, such as address information, within data packets.
How does an IP Network work?¶
The way Internet Protocol works is that information is transmitted over the network in discrete chunks called packets; each packet is mostly made up of whatever data the sender is trying to communicate, but also includes a header, consisting of metadata about the packet.
Three types of IP addresses used in a network:
Host Address: This address is unique to that individual and allows them to communicate one-to-one and with the network
Network Address: This is the first IP address in the network. This address gives you the hosts, who provide special network-related services, the ability to communicate with others.
Broadcast Address: This type of address allows the host to broadcast an announcement across the entire network.
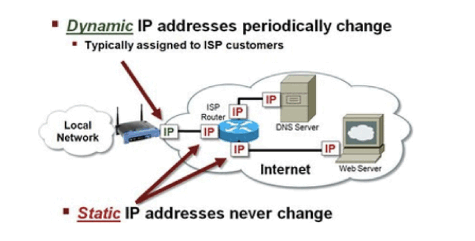
Difference between Static vs. Dynamic IP addresses¶
Static IP address is one that’s been assigned by an ISP to a device and is guaranteed to remain constant. If your computer’s address is 45.48.241.198, it will stay that way as long as you want it to. Static IP addresses are important for devices that need to be easily found on the internet, like web servers or gaming servers.
Dynamic IP address is basically handing out a new address to a device every time it connects to the network, and putting that address back into a pool of available addresses when the device disconnects. This technique helps conserve IP addresses.
Public IP Address vs. Private IP Address¶
A public IP address is the outward-facing (public-facing) IP address assigned to your router by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Your router uses its public IP to access the internet. Your public IP address identifies your device on the internet, and you can’t go online without one. It is used to communicate outside the network.
A private IP address is assigned by networks and routers to devices that are connected to them. It lets a router correctly direct traffic within its network, and private IPs also let devices wihtin a network communicate with one another.